Difference between revisions of "Contrib:KeesWouters/plate/variable pressure"
Keeswouters (Talk | contribs) m (→General way of determination of the pressure) |
Keeswouters (Talk | contribs) m (→General way of determination of the pressure) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
by Python commands. | by Python commands. | ||
This includes the y coordinate Ycog. The pressure depends on the centre y-value of each shell element. It is conveinient to use the added, last node of each shell element of the connectivity list. This node has been added in the Code-Aster command file by the MODI_MAILLAGE commnand to modify the QUAD8 to QUAD9 element. | This includes the y coordinate Ycog. The pressure depends on the centre y-value of each shell element. It is conveinient to use the added, last node of each shell element of the connectivity list. This node has been added in the Code-Aster command file by the MODI_MAILLAGE commnand to modify the QUAD8 to QUAD9 element. | ||
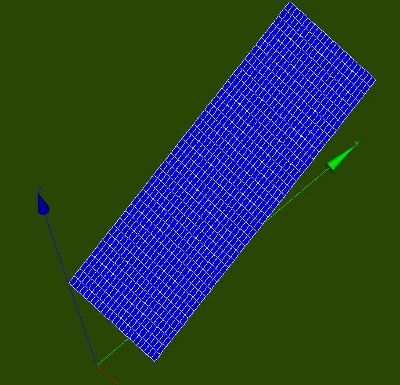
| − | The geometry and mesh is shown in the picture below. The main dimensions are: [x1, x2 | + | The geometry and mesh is shown in the picture below. The main dimensions are: [x1, x2; y1, y2; z1, z2] = [0.00,1.00; 0.00,3.00; 1.25,2.35], inclined plate in y direction. |
: [[Image:kw_varshell_geom.jpg]] | : [[Image:kw_varshell_geom.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 12:53, 13 January 2013
Contents
Varying pressure of shells - use of Python
If you are already familiar to Code Aster, enjoy this. If you are new to Code Aster have a look here first please.
A similar description for variable thickness of a plate is given in Contrib:KeesWouters/plate/thickness
november 2010 - SalomeMeca 2010 (Code Aster 10.2) - Ubuntu Meerkat 10.10 64bits.
January 2013 - update to Code Aster version 11.3 - Salome 6.6.0 - Linux Mint 14 Nadia
Static displacement of a shell under pressure
This is just a simple example of the use of shells (coque_3d) for static calculations. The main focus is on varying the pressure on a shell element by a Python list. The pressure on the shell depends on the average Ycog coordinate of the element. for mesh geometry, mesh and material property details see, once again, Contrib:KeesWouters/plate/thickness.
General way of determination of the pressure
The geometry and mesh are generated in Salome in the standard way. In Code Aster the mesh is read, including nodes number, node coordinates, element types and element connectivity. We use quadratic quad8 elements that are converted to quad9 (coque_3d) elements suitable for C-Aster.
Of each element
- determine the nodes are defined by the connectivity matrix,
- determine the coordinates of all the nodes and finally
- determine the centre of gravity and
- generate the thickness of the shell
by Python commands. This includes the y coordinate Ycog. The pressure depends on the centre y-value of each shell element. It is conveinient to use the added, last node of each shell element of the connectivity list. This node has been added in the Code-Aster command file by the MODI_MAILLAGE commnand to modify the QUAD8 to QUAD9 element. The geometry and mesh is shown in the picture below. The main dimensions are: [x1, x2; y1, y2; z1, z2] = [0.00,1.00; 0.00,3.00; 1.25,2.35], inclined plate in y direction.
Extraction of the coordinates
Among others, in Code Aster forum the procedure is discussed.
In Code Aster, after reading the initial mesh, the quad8 elements are converted to quad9 (coque_3d compatible) elements. This mesh is called meshmod (modified mesh) and is used as the basis for the further operations.